All activities required to generate electricity and distribute or sell gas or electricity to consumption outlets have an important environmental impact. EDP Spain has analyzed all environmental aspects and implemented measures for its prevention and minimization.
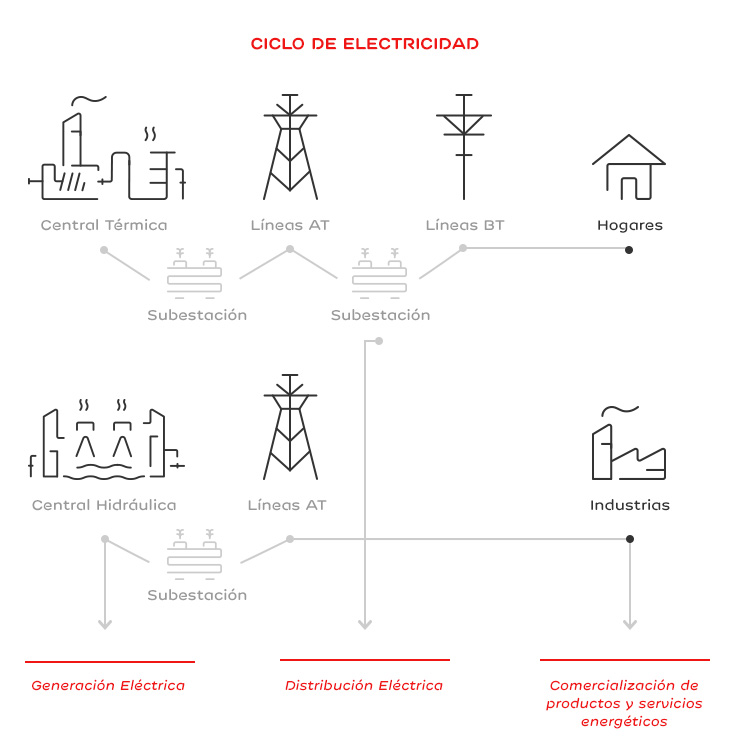

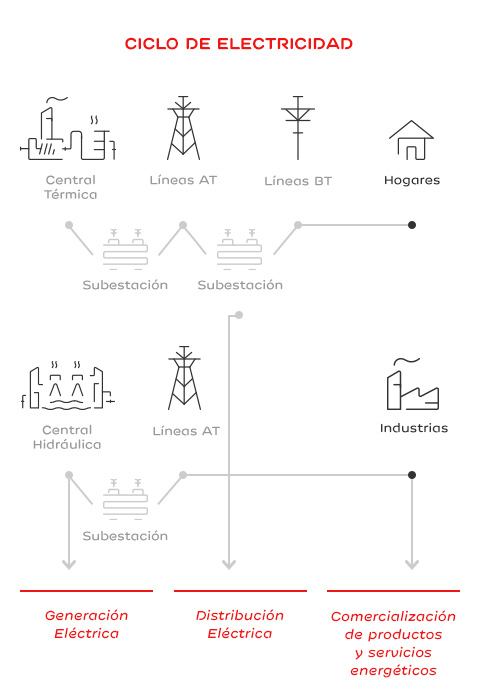


Electricity Generation
Thermal plants burn fuel in a boiler room and heat water to generate steam, which is expanded in a turbine, generating electricity in an alternator. As a result of combustion, gases are created, purified and finally eliminated through the chimney (emissions).
Carbon thermal plants also generate waste from combustion (ash and slag) and gypsum, a byproduct of gas desulfurization.
Another way to generate power is by using the rivers' hydraulic resources, where dammed water passes through a turbine, transforming the water’s potencial energy into mechanical energy, which in turn conveys energy to an alternator in order to produce electricity.
The main source of water used in our power plants are rivers, many of which located in protected areas or sensitive habitats and ecosystems.
As in any other industrial activity, all our facilities take all the necessary measures to adequately manage the soil and noise impact.
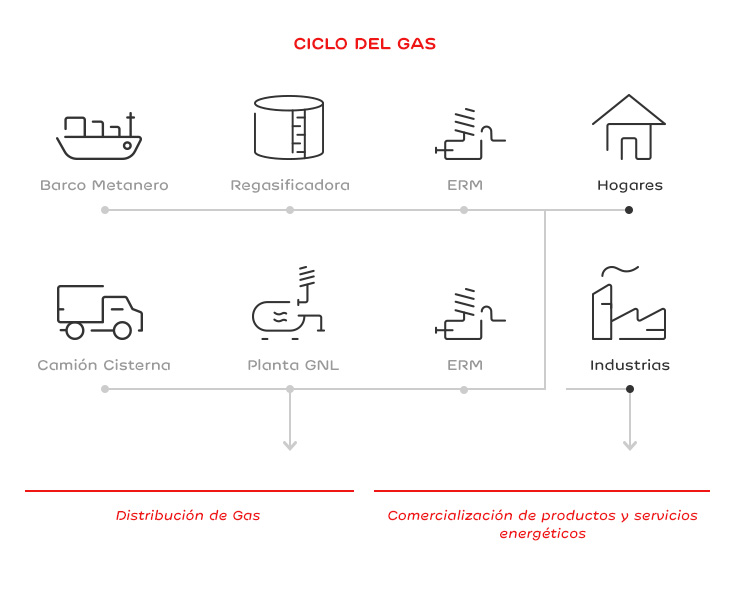
Gas and electricity distribution
The energy generated in our production centers is distributed by power lines until it reaches individual households and other consumers.
To reduce network losses, electricity voltage is increased in generation points and re-converted to medium or low voltage in facilities near consumption locations. To achieve this, transformers and other measurement and protection devices are used, located in substations, distribution centers and/or transformation centers.
These devices use mainly oil as a refrigerant; this ensures their proper maintenance in order to minimize waste production and avoid any accidental leak or spill.
The equipment used to cut and protect the main elements in the grid uses a dielectric agent, oil or sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), which is what makes cutting or extinction of the electric arc effective. Proper maintenance of such equipment is crucial, especially in the case of SF6, since it is a greenhouse gas.
In the case of gas distribution, it can be channeled from regasification plants or available satellite LNG plants, where liquefied natural gas is stored and distributed to consumption points. The regasification process requires a heat input, which is obtained by burning part of the stored natural gas in small-scale boilers, thus preventing the system from freezing.
To ensure energy supply in any location, networks are designed to have as little environmental impact as possible, although in some cases going through natural areas is inevitable.
These networks must be accessible, forcing us to cut down any large-scale vegetation that may grow around it. This measure significantly reduces the risk of fire in the case of electrical networks, preventing their contact with the surrounding vegetation.
Energy Trading
Energy trading is the sale of energy and value-added services to our customers: maintenance of the installation and household appliances, electronic billing, and other services to improve the installations' energy efficiency.